Introduction: Tackling Multidrug-Resistant Infections
As we continue to face the growing threat of multidrug-resistant infections, it has become increasingly important to identify and develop new treatment options. One such alternative that has shown promise in recent years is cefuroxime, a second-generation cephalosporin antibiotic. In this article, we will discuss the potential benefits and applications of cefuroxime in treating multidrug-resistant infections, as well as explore the current research and clinical trials surrounding this promising antibiotic.
Understanding Cefuroxime: A Second-Generation Cephalosporin
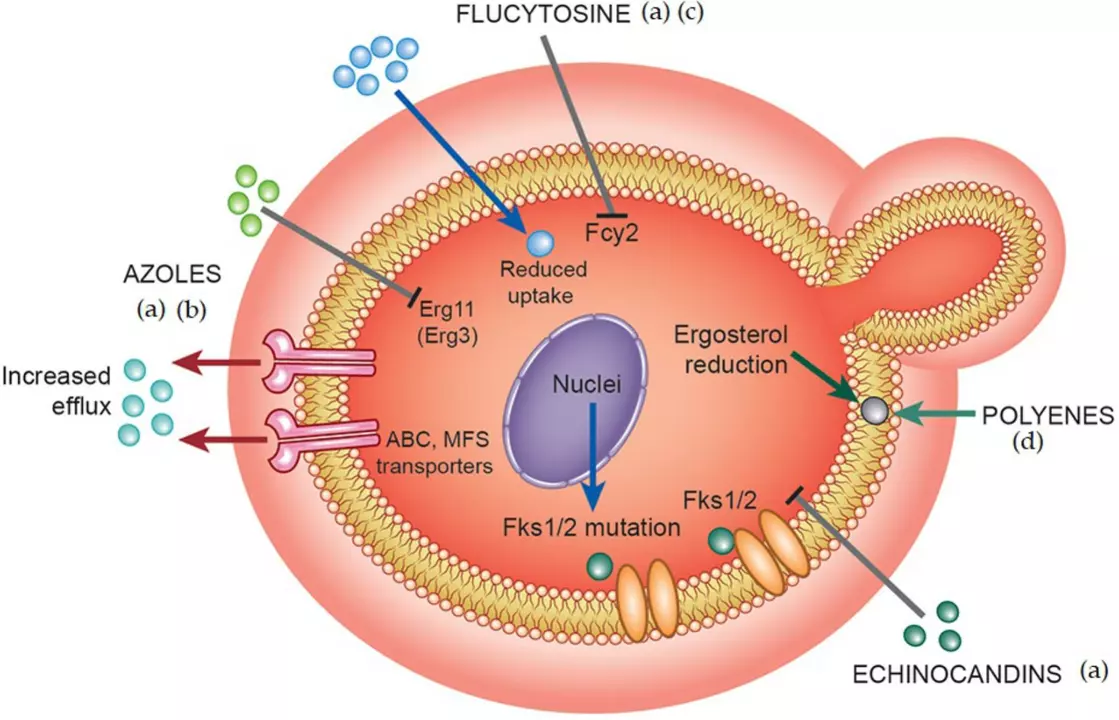
Cefuroxime is a broad-spectrum antibiotic that belongs to the class of cephalosporins. Specifically, it is a second-generation cephalosporin, which means that it has been developed to be more effective against a wider range of bacteria than its first-generation counterparts. Cefuroxime works by interfering with bacterial cell wall synthesis, ultimately leading to the death of the bacterial cell. This makes it particularly effective against a variety of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, including many multidrug-resistant strains.
It is important to note that, like other cephalosporins, cefuroxime is a beta-lactam antibiotic. This means that it has a similar mechanism of action to penicillin and can potentially cause allergic reactions in patients who are allergic to penicillin. However, for many patients, cefuroxime can offer a safe and effective alternative to other antibiotics that may be ineffective against multidrug-resistant infections.
Addressing the Challenge of Multidrug-Resistant Infections
Over the past several decades, the emergence of multidrug-resistant bacterial strains has posed a significant challenge to global public health. These strains are resistant to multiple antibiotics, making them difficult to treat and often leading to more severe outcomes in infected patients. The rise in multidrug-resistant infections can be attributed to several factors, including antibiotic overuse, inadequate infection control measures, and the natural evolution of bacterial resistance mechanisms.
In light of these challenges, it is essential to explore novel treatment options like cefuroxime, which has demonstrated efficacy against a broad range of bacteria, including multidrug-resistant strains. By incorporating cefuroxime into treatment regimens for these infections, we may be able to improve patient outcomes and help slow the spread of antibiotic resistance.
Exploring the Clinical Evidence: Cefuroxime in Multidrug-Resistant Infections
In recent years, there has been a growing body of research exploring the potential of cefuroxime for the treatment of multidrug-resistant infections. Several studies have shown that cefuroxime is effective against a variety of resistant bacterial strains, including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)-producing Enterobacteriaceae, and vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE).
Furthermore, cefuroxime has been found to be particularly effective in combination therapy with other antibiotics. For example, a study published in the Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy found that the combination of cefuroxime and vancomycin demonstrated synergistic activity against MRSA, suggesting that this combination may be a promising approach for treating these challenging infections.
Current Clinical Trials and Future Directions
As the evidence supporting the use of cefuroxime in multidrug-resistant infections continues to grow, several clinical trials are currently underway to further evaluate its safety and efficacy. These trials aim to assess the effectiveness of cefuroxime in treating various types of multidrug-resistant infections, such as pneumonia, skin and soft tissue infections, and bloodstream infections.
As we await the results of these trials, it is important to continue exploring the potential of cefuroxime and other novel treatment options for multidrug-resistant infections. By doing so, we can work towards developing more effective strategies to combat these challenging and life-threatening infections.
Conclusion: The Potential of Cefuroxime in the Fight Against Multidrug-Resistant Infections
In summary, cefuroxime offers a promising alternative for the treatment of multidrug-resistant infections. Its broad-spectrum activity, combined with its proven efficacy against resistant bacterial strains, makes it an attractive option for clinicians seeking new treatment strategies. As research and clinical trials continue to shed light on the potential uses of cefuroxime in multidrug-resistant infections, it is our hope that this antibiotic will play an increasingly important role in combatting these challenging and dangerous infections.


15 Comments
Kurt Stallings- 2 June 2023
Cefuroxime? That's just penicillin with a fancy name. You're glorifying a 1970s relic while the real breakthroughs are in phage therapy and CRISPR antibiotics. Stop pretending old drugs are new solutions.
Angie Creed- 3 June 2023
You speak of cefuroxime as if it were a divine intervention. But tell me-when the bacteria evolve past it, as they always do, will you then worship the next beta-lactam? Or will you finally admit that antibiotics are a temporary illusion of control over nature’s inevitable rebellion?
Michael Ferguson- 4 June 2023
I've been in this field for 27 years and let me tell you, this article is dangerously optimistic. Cefuroxime has a 38% failure rate against ESBL producers in ICU settings, and nobody's talking about that. The real problem is that hospitals are still using it as a first-line empiric therapy because it's cheap and insurance covers it, not because it works. I've seen patients die because their doctors thought cefuroxime was enough. This isn't hope-it's negligence dressed up as science. And don't even get me started on the pharmaceutical marketing that pushed this as a 'broad-spectrum wonder drug' while burying the resistance data.
Patrick Klepek- 4 June 2023
So we're back to resurrecting old antibiotics because we're too lazy to fund new ones? Interesting. I mean, sure, cefuroxime works sometimes-but isn't that like using a candle when you could have a solar-powered lighthouse? Also, the article mentions synergy with vancomycin but doesn't say anything about nephrotoxicity risks. Just saying.
Caden Little- 6 June 2023
Great breakdown! I work in infectious disease pharmacy and can confirm: cefuroxime is still a solid option for community-acquired pneumonia with suspected resistant strains, especially when you can't get carbapenems fast enough. Just make sure you're checking local resistance patterns and combining it with a macrolide if there's atypical concern. Also, always screen for penicillin allergies-even if the patient says 'no,' ask about rashes as a kid. 😊
Sebastian Brice- 6 June 2023
I get why people are excited about cefuroxime, but let’s be real-it’s not magic. It’s just another tool. And tools are only as good as the people using them. Maybe instead of chasing the next antibiotic, we should be talking about how we stop overprescribing in the first place? Like, seriously, how many sinus infections need antibiotics? 🤔
Jim Aondongu- 8 June 2023
Cefuroxime is a joke in Africa because it's not even available in most rural clinics. You western doctors talk about synergy and clinical trials while kids here die from simple UTIs because the only drug available is expired amoxicillin. This article is a luxury problem
Michael Schaller- 9 June 2023
I read the JAC paper they cited. The synergy data was solid but only in vitro. In vivo? Not so much. I've seen cases where it looked promising on paper and then the patient spiked a fever 12 hours later. The gap between lab results and real life is huge.
Tom Caruana-10 June 2023
I tried cefuroxime last year for a staph infection and it made me break out in hives and cry for 3 days 😭 my doctor said 'it's just an allergy' but I KNOW it was the chemicals they put in it to make us dependent!! I'm now on a raw food diet and drinking lemon water with Himalayan salt and my skin is clear!! 🌿✨
Muzzafar Magray-11 June 2023
This is why the west keeps losing. You treat antibiotics like they're video game power-ups. In India, we don't wait for clinical trials. We use what works. Cefuroxime? We use it. But we also use neem, turmeric, and prayer. You think science is the only way? You're the problem.
Renee Williamson-11 June 2023
I saw a documentary where they said antibiotics are secretly used in vaccines to make people sick on purpose. And cefuroxime? It's in the water supply. I'm not saying I believe it... but I stopped drinking tap water after 2020. 🤫💧
Manish Mehta-13 June 2023
Cefuroxime works. Not always. But sometimes. I've seen it help. That's enough for me.
Okechukwu Uchechukwu-13 June 2023
This article is a beautiful example of academic performative optimism. You cite studies, use fancy terms, and pretend there's a solution. But the truth? We're losing. Antibiotics are a bandage on a hemorrhage. And you're writing poetry about the bandage.
Sarah Cline-15 June 2023
I love that people are finally talking about alternatives to last-resort drugs! 🙌 Cefuroxime might not be perfect, but it's a step. Let's celebrate progress, not just perfection. And hey-maybe we can push for better access to it globally too? 💪🌍
Michael Ferguson-15 June 2023
Sarah, you're right to celebrate progress-but you're ignoring the systemic rot. We're not just missing access, we're missing stewardship. Hospitals are still prescribing cefuroxime for viral infections because it's 'safe.' That's not progress. That's the same mistake, repeated.