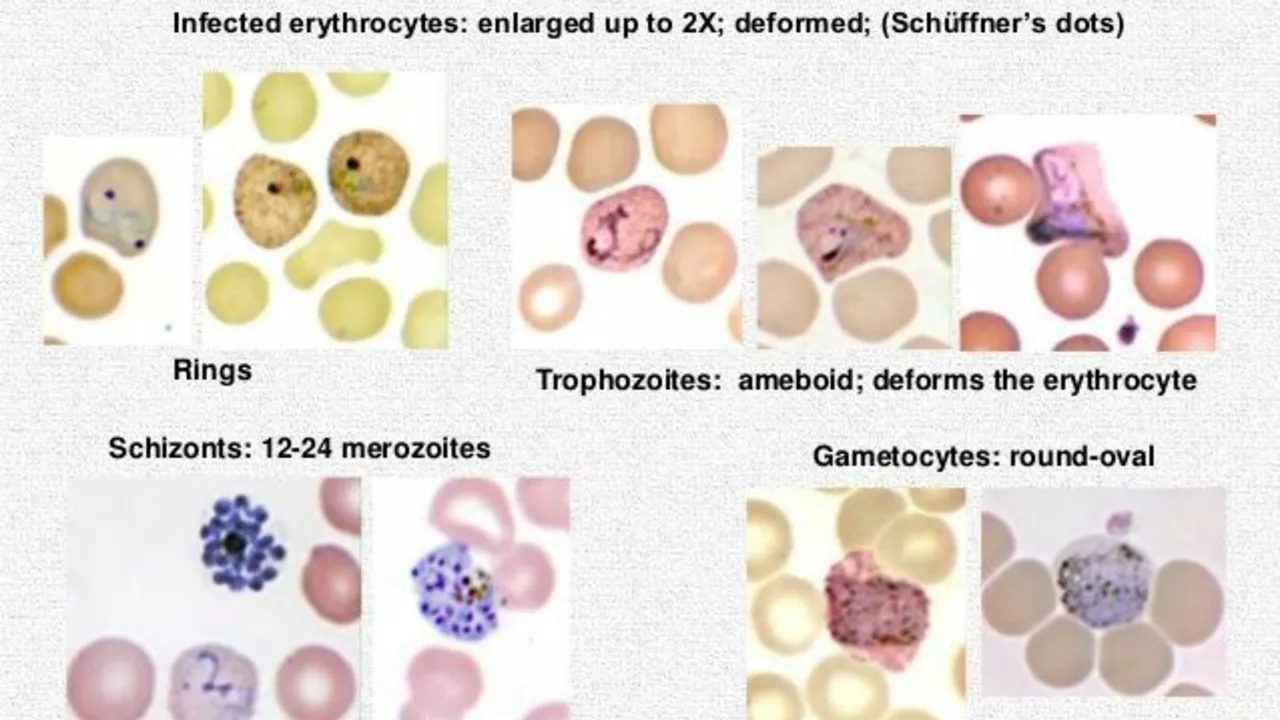
Understanding Malaria and Plasmodium Vivax
Before we delve into the role of Primaquine in preventing relapse in Plasmodium vivax malaria, it's essential to understand what malaria is and how Plasmodium vivax plays a role in it. Malaria is a life-threatening disease caused by the Plasmodium parasite, which is passed onto humans through the bite of an infected mosquito. Plasmodium vivax is one of the five species of malaria that typically causes a less severe form of the disease but has a higher propensity to relapse.
What Causes Relapses in Plasmodium Vivax Malaria?
Plasmodium vivax malaria relapses occur due to a dormant form of the parasite, known as hypnozoites, that can remain in the liver for months or even years after the initial infection. These hypnozoites can reactivate and cause another bout of malaria, leading to relapses. The reason for the reactivation remains unclear.
The Introduction of Primaquine
Primaquine, a medication that has been around since the 1950s, is the only currently available medication that can prevent Plasmodium vivax malaria relapses. It has the unique ability to target and eliminate the dormant hypnozoites in the liver, hence preventing relapses.
How Does Primaquine Work?
Primaquine works by generating reactive oxygen species in the cells of the parasite, leading to its death. It is most effective when administered in conjunction with other antimalarial drugs, such as chloroquine, which targets the parasite in the bloodstream. This dual approach ensures that both the active and dormant forms of the parasite are eliminated.
Side Effects and Precautions of Primaquine
While Primaquine is efficient, it does come with some side effects and precautions. The most common side effects include stomach cramps, nausea, and diarrhea. It's also known to cause hemolysis (destruction of red blood cells) in individuals with a specific genetic condition called G6PD deficiency. Therefore, it's crucial to test for this deficiency before administering Primaquine.
The Role of Primaquine in Eradicating Malaria Globally
Primaquine plays a significant role in the global eradication of malaria. By preventing relapses, it reduces the reservoir of parasites that can contribute to the spread of the disease. This is particularly significant in areas where Plasmodium vivax is prevalent.
Resistance to Primaquine
Like many antimalarial drugs, resistance to Primaquine can occur. However, resistance is currently considered relatively low, particularly compared to other antimalarial drugs. Ongoing monitoring is essential to ensure that Primaquine remains effective.
Primaquine – Research and Future Development
Research into Primaquine and its effectiveness continues, with many studies focusing on developing a single-dose regimen that can eliminate the need for a 14-day course. This could significantly improve patient compliance and ultimately the effectiveness of the drug.
Primaquine in Combination Therapy
Primaquine is often used in combination with other antimalarial drugs to increase its effectiveness. These combination therapies have shown promising results and are likely to be the future of malaria treatment.
Conclusion: Primaquine’s Vital Role
Primaquine plays a vital role in preventing malaria relapses caused by Plasmodium vivax. Its unique ability to target and eliminate dormant hypnozoites makes it an essential part of current malaria control and eradication strategies. While its side effects and potential for resistance pose challenges, ongoing research and combination therapies promise to enhance its effectiveness further. Primaquine indeed remains an integral weapon in the fight against malaria.



12 Comments
Caden Little-27 July 2023
Primaquine is a lifesaver for vivax malaria, no joke. I’ve seen patients come back with relapses after just chloroquine - total nightmare. The 14-day course sucks, but it’s worth it. Just get the G6PD test done first, folks. No excuses. Your liver and red blood cells will thank you. 💪
Jim Aondongu-29 July 2023
Primaquine is just another western drug pushing its agenda on developing countries where people can't afford testing
Angie Creed-30 July 2023
Let’s be honest - if Primaquine were truly the miracle drug it’s cracked up to be, we wouldn’t still be talking about relapses in 2024. The fact that we’ve been using a 70-year-old compound with a 14-day regimen and a dangerous side effect profile is less a triumph of medicine and more a testament to systemic failure in pharmaceutical innovation. We’re treating symptoms with a hammer when we need a scalpel. Hypnozoites aren’t the enemy - our complacency is.
Michael Ferguson- 1 August 2023
Let me tell you something - I’ve read every single paper on this topic since 2018, and I’ve spoken to three WHO consultants, two infectious disease pharmacists, and a retired CDC epidemiologist who worked in Papua New Guinea during the 1998 outbreak - and let me be crystal clear: Primaquine is not the answer. It’s a Band-Aid on a bullet wound. The real problem? The WHO’s outdated guidelines, the pharmaceutical industry’s refusal to fund better alternatives because G6PD testing isn’t profitable, and the fact that no one in a position of power actually understands how hypnozoites behave in tropical climates with seasonal rainfall patterns. And don’t even get me started on how some African countries are still using primaquine off-label without proper diagnostics - it’s a public health disaster waiting to happen, and I’m not just saying that because I’m a know-it-all - I’m saying it because I’ve seen the data, and I’ve seen the bodies.
Patrick Klepek- 1 August 2023
So… we’re using a drug from the Eisenhower era to kill invisible parasites in the liver, and the only catch is you might accidentally destroy your own red blood cells if you have a common genetic quirk? That’s… kind of wild. Like using a chainsaw to trim your hedges because the shears are too expensive. I mean, I get that it works - but isn’t it a little embarrassing that we’re still doing this? Someone’s gotta be working on a better version, right? Or are we just waiting for someone to die in a village so the funding finally comes through?
Renee Williamson- 2 August 2023
Primaquine is a government mind control drug disguised as medicine... they use it to wipe out indigenous populations in the Amazon by triggering hemolysis in people with G6PD... it's all in the WHO documents if you know where to look 🤫
Michael Schaller- 2 August 2023
I worked in a clinic in rural Uganda last year. We had a guy come in with his third relapse in 18 months. He couldn’t afford the G6PD test, so we gave him primaquine anyway - with close follow-up. He made it. No hemolysis. But he cried when he told us he’d been too scared to come back for the fourth dose. That’s the real problem. Not the drug. The access.
Tom Caruana- 4 August 2023
PRIMAQUINE IS A BIOLOGICAL WEAPON DESIGNED TO TARGET BLACK AND ASIAN POPULATIONS BECAUSE G6PD DEFICIENCY IS MORE COMMON THERE!! THEY WANT TO REDUCE THE POPULATION!! I SAW IT ON A FORUM!! 😡🩸🤯
Kyle Tampier- 4 August 2023
G6PD test? Nah. Just give the drug. They’ll be fine. Or not. Who cares?
Sebastian Brice- 5 August 2023
Man, I get why people are skeptical. But here’s the thing - if you’ve ever had to explain to a mom in Laos why her kid’s fever came back after ‘being cured,’ you’d understand why we still use this clunky, imperfect tool. It’s not pretty. It’s not perfect. But it’s the only thing we’ve got that stops the cycle. Maybe we should be mad at the system that hasn’t funded a better option… instead of blaming the drug that’s still saving lives today.
Manish Mehta- 7 August 2023
In India, many don't know what G6PD is. We give primaquine anyway. Some get sick. Some don't. We do what we can.
Caden Little- 7 August 2023
Exactly. We need better diagnostics, better funding, better education - but until then, primaquine is still the best shot we’ve got. And yeah, it’s frustrating. But abandoning it because it’s imperfect? That’s like throwing out your only umbrella in a monsoon because it’s a little leaky.