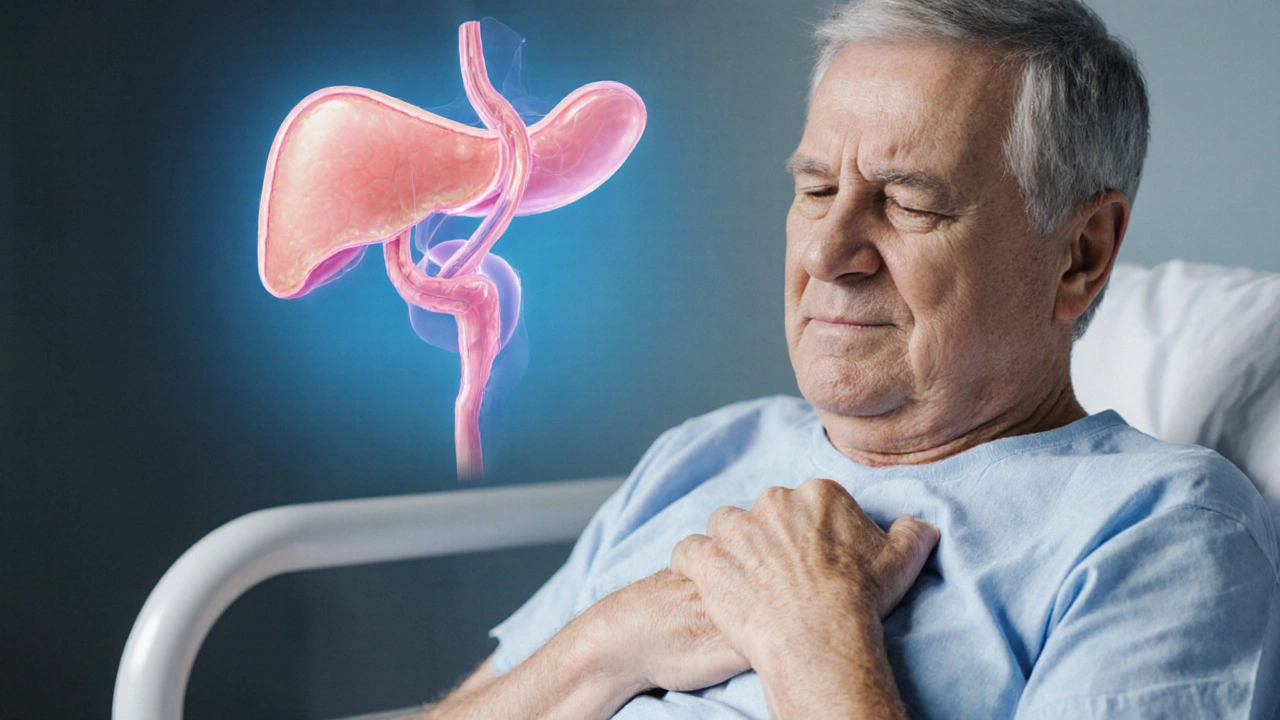
Pancreatic Duct Blockage: Causes, Symptoms & Treatment Options
When dealing with pancreatic duct blockage, a condition where the main duct that carries digestive enzymes from the pancreas becomes obstructed. Also known as PD blockage, it can trigger pain, jaundice, and inflammation. This blockage often leads to pancreatitis, inflammation of the pancreas that may range from mild discomfort to life‑threatening attack. In many cases, doctors turn to ERCP, Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography, a minimally invasive procedure that visualizes and clears the duct to restore flow. You’ll also see that biliary obstruction, a blockage of the bile ducts usually caused by gallstones or tumor pressure, frequently co‑exists with pancreatic duct blockage, worsening jaundice and liver stress. Finally, long‑term blockage raises the risk of pancreatic cancer, a malignant growth that often starts in the ductal cells and can be harder to detect early.
The relationship between these entities forms a clear chain: pancreatic duct blockage can cause pancreatitis, and both conditions may be aggravated by biliary obstruction. When the blockage persists, it creates an environment where cancerous cells can thrive. Understanding this chain helps doctors choose the right diagnostic tools—like abdominal CT, MRI, or ultrasound—to spot the problem early. Once identified, ERCP not only removes the obstruction but can also place a stent, keeping the duct open and reducing pressure on the pancreas and bile system.
What to Expect When Managing a Blocked Pancreatic Duct
First, doctors will assess symptoms such as severe upper‑abdominal pain, dark urine, or pale stools. Blood tests reveal elevated enzymes (amylase, lipase) and bilirubin, pointing toward duct issues. Imaging confirms the exact location of the blockage, whether it’s a stone, scar tissue, or tumor. If ERCP is feasible, it’s usually performed under sedation; a tiny camera guides a catheter to the blockage, and tools like balloons or baskets retrieve the obstruction. In cases where ERCP isn’t possible, surgeons might consider a pancreaticojejunostomy or other bypass techniques.
Recovery focuses on diet adjustments, enzyme supplementation, and regular monitoring for any sign of recurrent blockage or malignancy. Patients are often advised to limit fatty foods, stay hydrated, and follow up with imaging every few months. Lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking and maintaining a healthy weight, also lower the chances of future problems.
Below you’ll find a curated selection of articles that dive deeper into each aspect—symptom checklists, treatment comparisons, and prevention tips—so you can stay informed and take proactive steps toward better pancreatic health.
Pancreatic Duct Blockage: Signs You Need Immediate Medical Attention
Learn what pancreatic duct blockage is, its causes, warning signs, and exactly when to get medical help. Get clear guidance on diagnosis, treatment and next steps.