Primaquine: What It Is and When You Need It
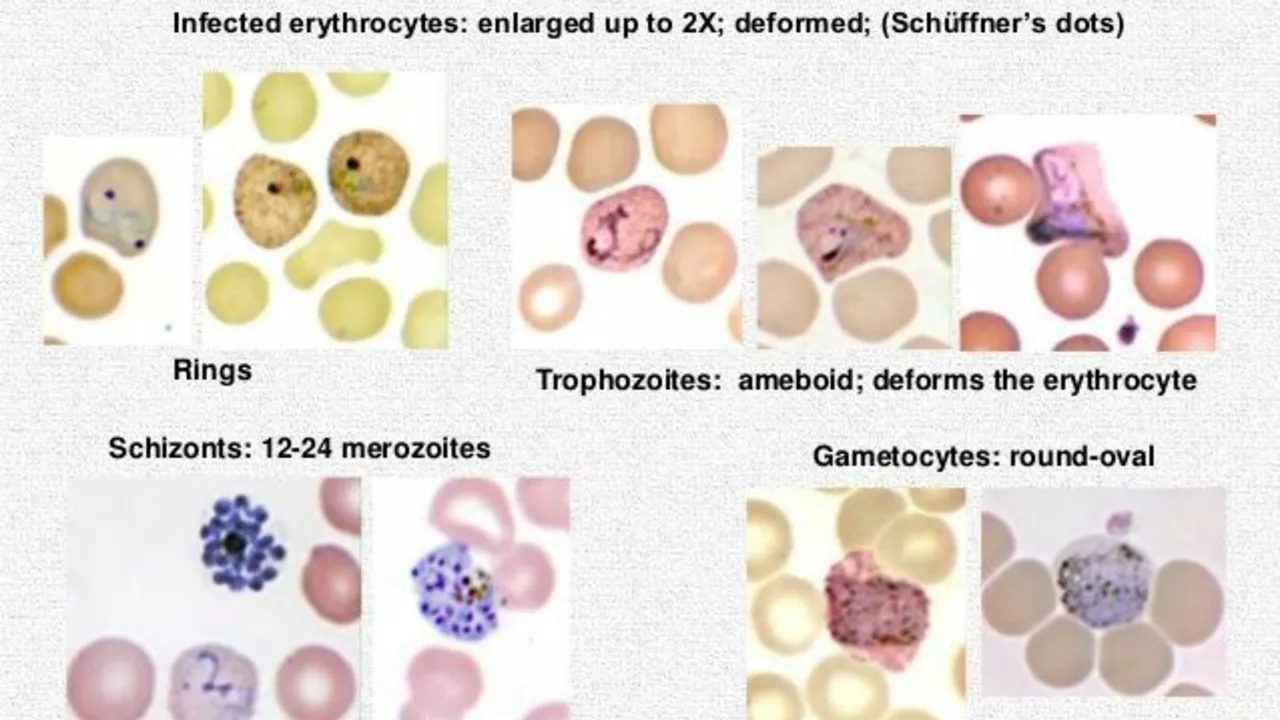
If you’ve ever heard of malaria treatment, chances are you’ve come across the name primaquine. It’s an antimalarial pill that targets the hidden liver stage of the parasite, which other drugs often miss. That makes it essential for preventing relapses after a bout of Plasmodium vivax or Plasmodium ovale infection.
Besides malaria, doctors sometimes use primaquine to stop certain types of lung infections and to treat a rare blood disorder called G6PD deficiency‑related hemolysis. But the most common reason people take it is to clear those dormant parasites that can cause a second wave of fever weeks after the first one.
How to Take Primaquina Safely
The usual adult dose for malaria relapse prevention is 15 mg (or 30 mg if you weigh over 70 kg) taken once a day for 14 days. Kids get a weight‑based dose, so it’s best to follow the doctor’s exact instructions.
Before you start, your doctor will check your G6PD levels. If you’re deficient, primaquine can cause serious anemia, so they might avoid it or use a lower dose. Always tell your pharmacist about any other meds you take – especially antacids, blood thinners, or drugs that affect the heart rhythm.
Take the pill with food if it upsets your stomach, and try to keep the timing consistent each day. Missing doses can let parasites survive, which defeats the purpose of the treatment.
Common Side Effects & When to Seek Help
Most people tolerate primaquine well, but a few side effects pop up. The most frequent are nausea, stomach cramps and mild headache. These usually fade after a day or two.
If you notice dark urine, yellow‑tinged skin, sudden fatigue, or shortness of breath, stop the medication and call your doctor right away – those could be signs of hemolysis in people with G6PD issues.
Allergic reactions are rare but can happen. Look out for rash, itching, swelling of the face or throat, and seek medical help immediately if any appear.
To keep things smooth, keep a simple log of when you take each dose and any symptoms you feel. Share that log with your healthcare provider at follow‑up appointments – it helps them spot patterns early.
In summary, primaquine is a powerful tool against malaria relapses if used correctly. Check your G6PD status, stick to the prescribed schedule, watch for side effects, and stay in touch with your doctor. With these steps, you can clear those hidden parasites and stay healthy on your travels or after treatment.
The role of Primaquine in preventing relapse in Plasmodium vivax malaria
Primaquine plays a crucial role in the fight against Plasmodium vivax malaria, specifically in preventing relapses. This medication is known for its ability to target the dormant liver stages of the parasite, effectively preventing it from reactivating and causing a recurrence of the disease. It's essentially a game-changer in malaria treatment due to its unique mechanism of action. However, it's important to note that it may cause side effects in individuals with certain genetic conditions. Therefore, it's always necessary to use Primaquine under a healthcare provider's supervision.